Aranea framework consists of a number of independent components each
performing a single well-defined function. Aranea uses Spring to wire
these components into a working framework. Though other IoC containers and
configuration frameworks would also work we support Spring by default
since it provides a very comfortable and versatile syntax for configuring
beans. The dispatcher servlet that uses Spring is called
org.araneaframework.integration.spring.AraneaSpringDispatcherServlet.
Note that Aranea itself does not depend on Spring except the classes in
the org.araneaframework.integration.spring
package.
The simplest way to configure Aranea for a web application is to
set the araneaApplicationStart init parameter of the
dispatcher servlet to the starting widget or flow of the application:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd">
<web-app>
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.araneaframework.http.core.StandardSessionListener
</listener-class>
</listener>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>araneaServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.araneaframework.integration.spring.AraneaSpringDispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>araneaApplicationStart</param-name>
<param-value>example.StartWidget</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>araneaServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/main/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
This configuration will load Aranea using
example.StartWidget as the application starting
point.
Note
The servlet must be mapped to a all subpathes starting from
some prefix (in our case /main/*) so that Aranea
could do some path-dependent operations like extension file
importing.
Note
org.araneaframework.http.core.StandardSessionListener
is required to allow Aranea to process events like session
invalidation.
Aranea can also be configured using a Spring configuration file
located in /WEB-INF/aranea-conf.xml. Particularly it
may be used to set the starting widget instead of the init-parameter:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING//DTD BEAN//EN"
"http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans.dtd">
<beans>
<bean id="araneaApplicationStart"
class="example.StartWidget"
singleton="false"/>
</beans>
This seems to be more verbose, but it also allows to configure the framework components as described in Section 3.4, “Framework Configuration”.
Aranea also takes into account a property file located in
/WEB-INF/aranea-conf.properties. The following
properties are recognized:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
l10n.resourceBundle | The base name of the resource bundle used for
localization. This value isn't used if default
araneaLocalizationFilter is overidden (e.g.
by the SpringLocalizationFilterService)
Default value:
|
l10n.defaultLocale | The default locale to be used in the application.
Default value:
|
l10n.encoding | The default character encoding to be used throughout
the application (e.g. for request and response).
Default value:
|
jsp.path | The path from the webapp root to the directory that
will act as JSP root. The JSPs put there can be selected using
widget view selectors (see Section 2.7.7, “View Model and Rendering”). Default value:
|
AraneaSpringDispatcherServlet provides a number
of init-params that allow to further customize Aranea configuration:
| init-param | Description |
|---|---|
araneaCustomConfXML | The custom location of a Spring XML file used to
configure Aranea. Default
value:
|
araneaCustomConfProperties | The custom location of a property file used to
configure Aranea. Default
value:
|
araneaApplicationStart | The class name of an Aranea widget that will serve as
the starting point of an Aranea application. If omitted the
Spring bean araneaApplicationStart will be
used. |
araneaApplicationRoot | The class name of an Spring bean describing an Aranea
component that will serve as the framework root. If omitted
the Spring bean araneaApplicationRoot will
be used. Can be used to override the default configuration
altogether. |
Currently, the most common way to put Aranea to work is to host it
in a Servlet 2.3 or compatible container. The most generic way to do
that is to extend the
org.araneaframework.http.core.BaseAraneaDispatcherServlet
and build the root component of type
org.araneaframework.http.ServletServiceAdapterComponent
in the overrided method buildRootComponent():
package com.foobar.myapp;
class MyServlet extends BaseAraneaDispatcherServlet {
protected ServletServiceAdapterComponent buildRootComponent() {
StandardServletServiceAdapterComponent root = new StandardServletServiceAdapterComponent();
//Configure the child components, service widgets using setter injection
//...
return root;
}
}
And one can then use such a servlet to configure Aranea in a web application as usually replacing the standard dispatcher servlet with our custom one.
Aranea framework is made up of the same Components, Services and Widgets that are also used to develop Aranea applications. Each component performs a single well-defined function and may depend on other components only via Environment. The framework components mostly fall in one of the three following categories:
- Filter
Filter components are the simplest. The component contains a single unnamed child and implements the Filter pattern by either passing each call to the child or not. However in addition it may enrich the child's environment with contexts and provide more functionality like exception handling or synchronization. Typical examples of filters are localization filter (provides a localization context), synchronization filter (synchronizes on
action()method) and transactional filter that does not let through double submits.- Router
Router typically contains many named children, and chooses only one to propagate the calls to according to some
InputDataparameter. Router may have the children either statically preconfigured or created dynamically when the request comes (the latter is the case with session service router). It may also allow us to add/remove children while the application is running. A typical application of a router is to distinguish among major application parts by some attribute (like component corresponding to a user session, or one of the popup window of current user).- Container
Container can have one or many children, but it typically will do more with them than just passing the calls to one of them. A typical example is the widget container service which translates
action()calls into widgetupdate()/event()/process()/render()cycle.
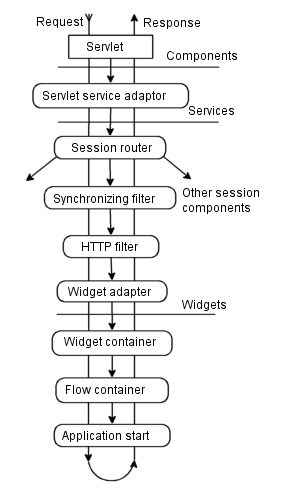
The frameworks itself is assembled using a hieararchy of components (this hierarchy is mostly flat, except for the routers and application components). The hierarchy is arrange simply by containment, with each component containing its chidren as fields as illustrated on Figure 3.1, “Framework assembly example”.
Of course this illustration is simplified, omitting most of the components described in Section 3.5, “Framework Components”. If you want to find out more about the way framework is built and assembled, see the Aranea Technical Paper.
Aranea framework is assembled into a mostly-flat hierarchy using
Spring beans. The default Aranea configuration is loaded by the
AraneaSpringDispatcherServlet, but it can be overriden
with the custom configuration in aranea-conf.xml. The
dispatcher servlet loads the configuration in such a way that same named
beans in aranea-conf.xml override the ones specified in
the default configuration. However, not all beans can be safely or
comfortably overriden, since many of them will also refer to their child
beans.
It is always safe to override filters, as they should never refer directly to their children. To override a filter just make a bean definition with the same name as in default configuration (filters and their default configuration names among other components are described in Section 3.5, “Framework Components”). For instance to override the default localization context with a custom-made one, one would need to add the following lines:
<bean class="example.LocalizationFilterService"
id="araneaLocalizationFilter" singleton="false">
<property name="languageName" value="ee"/>
</bean>
There is no good way in Spring to undefine a bean, so instead we use a "No OPeration" filter to nullify a filter from the default configuration:
<bean class="org.araneaframework.framework.core.NopFilterWidget"
id="araneaTransactionFilter" singleton="false"/>
Warning
Since filters can be both services and widgets, you have to be
careful to use the appropriate one for the current context. In current
case you have override service filters with
NopFilterService and widget filters with
NopFilterWidget.
There is no generic way to insert filters into an arbitrary place in the framework component hierarchy. However there are several predefined places left for optional bean insertion at various levels of the hierarchy, which should cover most of customization needs. To allow inserting more than one filter at a time a filter chain bean is provided that allows putting together an arbitrary long chain of filters:
<bean id="araneaCustomSessionFilters" singleton="false"
class="org.araneaframework.framework.filter.StandardFilterChainService">
<property name="filterChain">
<list>
<ref bean="araneaSerializingAudit"/>
<ref bean="myCustomFilter1"/>
<ref bean="myCustomFilter2"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
Note
Use StandardFilterChainService for hosting
service filters and StandardFilterChainWidget for
hosting widget filters.
Follows a description of the insertion point beans and their scope:
| Bean name | Scope and Description |
|---|---|
araneaCustomApplicationFilters | These filters are created only once and live as long as the application does. They are not synchronized and should be use to add features generic to the whole application, not specific users. The exceptions thrown by this filters are intepreted as critical and are handled by the critical exception handler. Examples: araneaFileUploadFilter, araneaStatisticFilter. |
araneaCustomSessionFilters | These filters are created for every HTTP user session and live as long as the session does. They are generally synchronized and should be used to add features specific to the current user session. Examples: araneaLocalizationFilter. |
araneaCustomThreadFilters | These filters are created for every user browser window and live as long as the window does. They are synchronized and should be used to add features specific to the individual browser window (e.g. most rendering filters will fall into this category). Examples: araneaThreadCloningFilter . |
araneaCustomWidgetFilters | These filters are created for every user browser window and live as long as the window does. They are synchronized and should be used to add features specific to the individual browser window. Unlike the rest of the filters this can be widgets and thus can take advantage of the widget update/event/process/render cycle. Examples: araneaTransactionFilter, araneaMessagingFilter. |
Aranea configuration is determined by request-processing components that can be assembled in many different ways. Following sections are a brief reference for pre-existing standard components, most of which are also used in Aranea framework default configuration.
| Java class: | StandardLocalizationFilterService |
| Default configuration name: | araneaLocalizationFilter |
| Provides: | LocalizationContext |
| Depends on: | - |
Provides localization services to children. See Section 2.8.2, “LocalizationContext”.
| Injectable properties | Description |
|---|---|
| languageName | A valid ISO Language Code. Sets Locale
according to given language. |
| resourceBundleName
| Name of the used resource bundle used to localize the application. |
| locale
| Locale to use. Either that or
languageName should be specified, but not
both. |
| Java class: | StandardUpdateRegionFilterService |
| Default configuration name: | araneaUpdateRegionFilter |
| Provides: | - |
| Depends on: | - |
When serving AJAX requests made with AjaxAnywhere (see Section 9.1.2, “AjaxAnywhere (http://ajaxanywhere.sourceforge.net/)”), extracts from the initial response these page regions that need to be updated (request includes the names of these regions), then modifies the response to include just these regions (not the whole page).
| Injectable properties | Description |
|---|---|
| characterEncoding
| The character encoding for responses served by this filter, default being "UTF-8". |
| existingRegions
| When the filter is activated, it tries to extract
specified regions from response, even if they were not
explicitly asked to be updated in request. This is useful for
always updating some common page regions (feedback message
regions etc). Some default region names that should be updated
when AJAX request is made are messages,
popupRegistrationRegion. |
| Java class: | StandardContextMapFilterWidget |
| Default configuration name: | araneaEnvContextFilter |
| Provides: | - |
| Depends on: | - |
Filter widget that enriches children environment with specified context entries.
| Injectable properties | Description |
|---|---|
| contexts | A map of contexts that will be added to environment. The keys can contains strings of kind "package.ClassName.class", which will use a Class object of the specified classname as the context key. The context value should be an object instance of the context interface. By convention a context should be registered under a key that is an interface it implements. |
| Java class: | StandardCriticalExceptionHandlingFilterService |
| Default configuration name: | araneaCriticalErrorHandler |
| Provides: | - |
| Depends on: | - |
Catches the exceptions (if any) occuring while executing children
methods; passes the exceptions on to Service that
deals with exception handling (obtained from
ExceptionHandlerFactory).
| Injectable properties | Description |
|---|---|
| exceptionHandlerFactory
| A factory for creating exception handlers. An exception handler is a service, which handles the user notification and recovery. |
| Java class: | StandardCriticalExceptionHandlingFilterService |
| Default configuration name: | araneaFileUploadFilter |
| Provides: | FileUploadContext,
FileUploadInputExtension |
| Depends on: | - |
Enriches child environment with
FileUploadContext (which is just a marker interface).
When incoming request is multi-part request, children's
InputData is extended with
FileUploadInputExtension that allows children easy
access to uploaded files.
| Injectable properties | Description |
|---|---|
| multipartEncoding
| Character encoding that will be used to decode the
multipart/form-data encoded strings. The
default encoding is determined by Apache
Commons FileUpload class. |
| useRequestEncoding
| When set to "true" request character encoding will be
used to parse the multipart/form-data encoded
strings. |
| maximumCachedSize
| Maximum size of file that may be cached in memory. |
| maximumSize
| Maximum size of file that may be uploaded to server. |
| maximumRequestSize
| Maximum size of the request that server will parse to the end. |
| tempDirectory
| Temporary directory to use when uploading files. |
| Java class: | StandardHttpResponseFilterService |
| Default configuration name: | araneaResponseHeaderFilter |
| Provides: | - |
| Depends on: | - |
Filter that sets necessay headers of the response.
| Injectable properties | Description |
|---|---|
| cacheable | Whether the response is cacheable or not. By default it is not cacheable. |
| contentType
| Sets the content type of the response. Default is "text/html; charset=UTF-8". |
| cookies
| Constructs cookies from the <cookieName, cookieValue> pairs in the map and sets them in response. |
| headers
| Sets the headers of the response from the map of <headerName, headerValue>. |
| cacheHoldingTime
| Sets the cache-control's max-age parameter, value is in milliseconds. Response must be cacheable for this to have any effect. |
| Java class: | StandardJspFilterService |
| Default configuration name: | araneaJspConfigFilter |
| Provides: | JspContext |
| Depends on: | LocalizationContext |
Provides JSP specific information to children.
| Injectable properties | Description |
|---|---|
| submitCharset | Sets the "accept-charset" attribute value that will be used for rendering Aranea JSP specific systemForm. |
| jspPath
| Path where widgets rendering themselves with jsp templates should search for them. Default is "/WEB-INF/jsp". |
| jspExtension
| File name extension jsp templates are assumed to have. Default is ".jsp". |
| Java class: | StandardMessagingFilterWidget |
| Default configuration name: | araneaMessagingFilter |
| Provides: | MessageContext |
| Depends on: | - |
| Java class: | StandardPopupFilterWidget |
| Default configuration name: | araneaPopupFilter |
| Provides: | PopupWindowContext |
| Depends on: | ThreadContext,
TopServiceContext,
TransactionContext |
Provides methods for opening new session-threads and renders these in different browser windows at client-side.
| Injectable properties | Description |
|---|---|
| threadServiceFactory
| Factory that should build the component chain according to effective Aranea configuration, beginning with sessionthread-level filters. |
| Java class: | StandardSerializingAuditFilterService |
| Default configuration name: | araneaSerializingAudit (not included
in default filter chain) |
| Provides: | - |
| Depends on: | - |
Serializes the the session during the request routing. This filter helps to be aware of serializing issues during development as when the session does not serialize, exception is always thrown. In production configuration, this filter should never be enabled, thus it is disabled by default.
| Injectable properties | Description |
|---|---|
| testXmlSessionPath
| The path where the serialized sessions should be logged in XML format. If not specified, serialization tests are performed in-memory. |
| Java class: | StandardStatisticFilterService |
| Default configuration name: | araneaStatisticFilter |
| Provides: | - |
| Depends on: | - |
Filter that logs the time it takes for the child service to serve the request (complete its action method).
| Injectable properties | Description |
|---|---|
| message
| The prefix of the statistics log statement. |
| Java class: | StandardSynchronizingFilterService |
| Default configuration name: | araneaSynchronizingFilter |
| Provides: | SynchronizingContext |
| Depends on: | - |
Synchronizes the calls to its child widget. Enriches environment
with SynchronizingContext (which is just marker
interface).
| Java class: | StandardThreadCloningFilterService |
| Default configuration name: | araneaThreadCloningFilter |
| Provides: | ThreadCloningContext |
| Depends on: | ThreadContext,
TopServiceContext |
Implementation of a service that clones currently running session thread upon request and sends a response that redirects to cloned session thread. It can be used to support "open link in new window" feature in browsers. Cloning is generic and resource demanding, as whole tree of session thread components is recreated. Custom applications may find that they can implement some application specific cloning strategy that demands less memory and processing power.
| Injectable properties | Description |
|---|---|
| timeToLive
| Inactivity time for cloned thread after which thread router may kill the thread service. This is specified in milliseconds. If unset, threads created by cloning service usually live until HTTP session in which they were spawned expires. |
| Java class: | StandardTransactionFilterWidget |
| Default configuration name: | araneaTransactionFilter |
| Provides: | TransactionContext |
| Depends on: | - |
TransactionContext implementation that
filters routing of duplicate requests. The detection of duplicate
requests is achieved through defining new transaction ID in each
response and checking that next request submits the consistent
transaction ID. Missing (null) transaction ID is
always considered inconsistent. For purposes of asynchronous requests,
override transaction ID is always considered
consistent.
| Request parameter name | Description |
|---|---|
transactionId | Transaction id must be equal to the last one generated for the transaction to be consistent. |
| Java class: | StandardClassReloadingFilterWidget |
| Default configuration name: | - |
| Provides: | - |
| Depends on: | - |
This filter allows to reload the underlying object classes
dynamically. This means that you can just change the widget source file,
compile it (e.g. with IDE built-in compiler) and it will be reloaded
seamlessly in Aranea. This will apply only to Aranea widget classes
under this filter and the classes they contain (but not e.g. Spring
beans). This filter must be registered instead of the
araneaApplicationStart to function.
Warning
None of the classes under this filter may be configured by Spring or anything else using its own classloader!
| Injectable properties | Description |
|---|---|
| childClass
| The full names of the child widget class. |
| Java class: | StandardClientStateFilterWidget |
| Default configuration name: | araneaClientStateFilter (not included
in default filter chain) |
| Provides: | - |
| Depends on: | - |
This filter will serialize the state of underlying widgets onto client-side. This significantly decreases the server-side session size and thus memory use. It is especially useful in intranet applications with lots of spare bandwidth. The filter should be positioned as the first custom widget filter for most gain.
Note
The filter will protect against tampering with the serialized state and will throw an exception if modified state is submitted from the client-side. As a bonus this filter will also allow a user to make up to 10 steps back and forward in browser history, restoring the correct state.
| Injectable properties | Description |
|---|---|
| compress
| If true the serialized state will also be GZIP'ed, trading processor time for bandwidth. False by default. |
| Java class: | StandardFileImportFilterService |
| Default configuration name: | araneaFileImportFilter |
| Provides: | - |
| Depends on: | - |
This filter is responsible for providing a virtual file system so that extensions could make use of the resources included in .JAR files. See Section 3.6.1, “Extension Resources”
| Java class: | StandardMountingFilterService |
| Default configuration name: | araneaMountingFilter |
| Provides: | MountContext |
| Depends on: | - |
Implementation of a service that allows to "mount" flow components to a publicly accessible URL. It is used when it is needed that some (read-only) parts of application are accessible to users who are not able to enter the session-based conversation with application.
| Injectable properties | Description |
|---|---|
| mounts
|
Keys in the map are URL prefixes under which the flow component is mapped.
Values are org.araneaframework.Message factories of type MountContext.MessageFactory—producing
messages that generate component hierarchy for serving wanted content.
|
| Java class: | RootFlowContainerWidget |
| Default configuration name: | araneaRootFlowContainer |
| Provides: | RootFlowContext,
FlowContext |
| Depends on: | - |
See Section 2.8.3, “FlowContext” for purpose and philosophy
behind FlowContext.
RootFlowContext is same as
FlowContext, but allows to acces the root flow
container at any time.
Tip
Flow containers are not generally a part of the framework and
can be used in your application as needed. In a typical Aranea
application the menu will inherit from
ExceptionHandlingFlowContainerWidget that besides
providing the flow container functionality also allows to handle
flow exceptions inside the container, preserving the menus and
current state. See business application tutorial for more
information.
| Injectable properties | Description |
|---|---|
| top
| First widget to be started in this container. |
External resources, such as javascript, style and image files of
Aranea components are managed through different configuration files. The
resources are listed in XML files and can be accessed through
StandardFileImportFilterService. This approach makes
it possible to package all the resources into the aranea
jar archives and no manual copying of necessary files
to fixed locations is needed.
Aranea comes bundled with a
aranea-resources.xml file which defines all the
external resources.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<resources>
<files content-type="text/css" group="defaultStyles">
<file path="styles/_styles_global.css"/>
...
<file path="styles/_styles_screen.css"/>
</files>
<files content-type="image/gif">
<file path="gfx/i01.gif"/>
...
<file path="gfx/i02.gif"/>
</files>
...
</resources>
All the files listed in the configuration
files are allowed to be loaded through the
FileImportFilter. Some are grouped by name to provide
an easy access for reading files in bulk.
To override specific files in the
configuration file, the new file should be placed in a subdirectory
override. When loading a file, Aranea first trys to
open the file in the override directory and on
failure trys to read the file without the prefix directory.
To add files to the defined list, construct a
configuration file and name it aranea-resources.xml.
All such configuration files from the classpath are parsed for the
resources. If two file groups are defined with the same name, the group
is formed by taking a union from the files in the group.
Groupnames defaultStyles and
defaultScripts are predefined groups for managing the
necessary core files that must be included for Aranea to work
correctly.
For custom loading a resource, the URL to use is
/fileimporter/filepath. The
fileimporter is
StandardFileImportFilterService.FILE_IMPORTER_NAME
and filepath is the path that is defined for the file
in the resource configuration file.
Extensions of the framework provide their own configuration files for configuring their resources. New extensions cannot be defined right now on the fly.